George Peabody
George Peabody provided benefactions of well over $8 million ($158,000,000 in 2017 dollars), most of them in his own lifetime. Among the list are:
1852 The Peabody Institute (now the Peabody Institute Library), Peabody, Mass: $217,000
1856 The Peabody Institute, Danvers, Mass (now the Peabody Institute Library of Danvers): $100,000
1857 The Peabody Institute (now the Peabody Institute of the Johns Hopkins University), Baltimore: $1,400,000. By including a complex involving a library, an academy of music, and an art gallery, his goal was to promote the moral, intellectual and artistic opportunities for the People of Baltimore.
1862 The Peabody Donation Fund, London: $2,500,000
1866 The Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard University: $150,000
1866 The Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University: $150,000 (at the suggestion of his nephew Othniel Charles Marsh, son of his younger sister Mary Peabody and America’s first professor of paleontology)
1867 The Peabody Academy of Science, Salem, Mass: $140,000 (now the Peabody Essex Museum) 1866 The Georgetown Peabody Library, the public library of Georgetown, Massachusetts
1866 The Thetford Public Library, the public library of Thetford, Vermont: $5,000
1901 The Peabody Memorial Library, Sam Houston State University, Texas
1913 George Peabody Building, University of Mississippi
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Harmony Grove Cemetery
30 Grove Street
Salem, Massachusetts, 01970
USA
North America
Map:
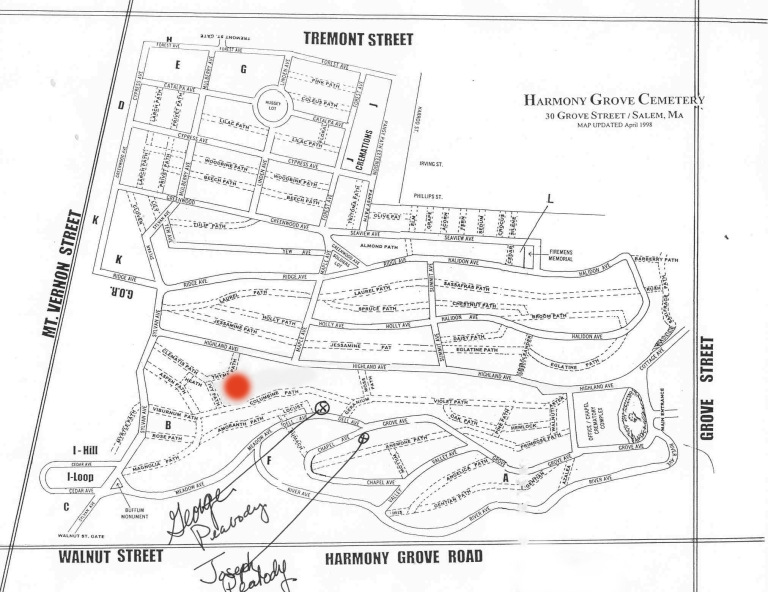
Grave Location:
Peabody Family PlotGrave Location Description
As you enter the cemetery turn left at the chapel and follow it around making the second right. His grave can be found up the step hill on your right 200 feet after making the right turn.
And despite numerous claims on other “grave-oriented” websites – this is not a cenotaph. George Peabody and some of his family members are really, truly buried here.





