Joan Merriam Smith
The Crash
Witnesses said that the airplane had been flying normally, estimated at between 1,000 and 2,000 feet (305–610 meters) above the mountainous terrain, when the right wing folded back along the fuselage. The airplane, with the engine revving, went into a dive and crashed into the north slope of Blue Ridge, a few miles west of Wrightwood, California, 10–12 seconds later. There was an explosion and fire and both Joan Merriam Smith and Trixie Ann Schubert were killed instantly.
Investigators found that both wings had failed outboard of the struts. The outer wing panels, both ailerons and the left elevator were located approximately 1½ miles from the point of impact. Examination showed that the aircraft had suffered severe loads. “There was no evidence of fatigue or failure of the aircraft before the inflight structural failure.”
The Civil Aeronautics Board reported the Probable Cause: “The pilot entered an area of light to moderate turbulence at high speed, during which aerodynamic forces exceeding the structural strength of the aircraft caused in-flight structural failure.” According to the CAB, the Cessna 182 had an airspeed in excess of 190 miles per hour when it entered the area of turbulence.
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Forest Lawn Memorial Park
4471 Lincoln Avenue
Cypress, California, 90630
USA
North America
Map:
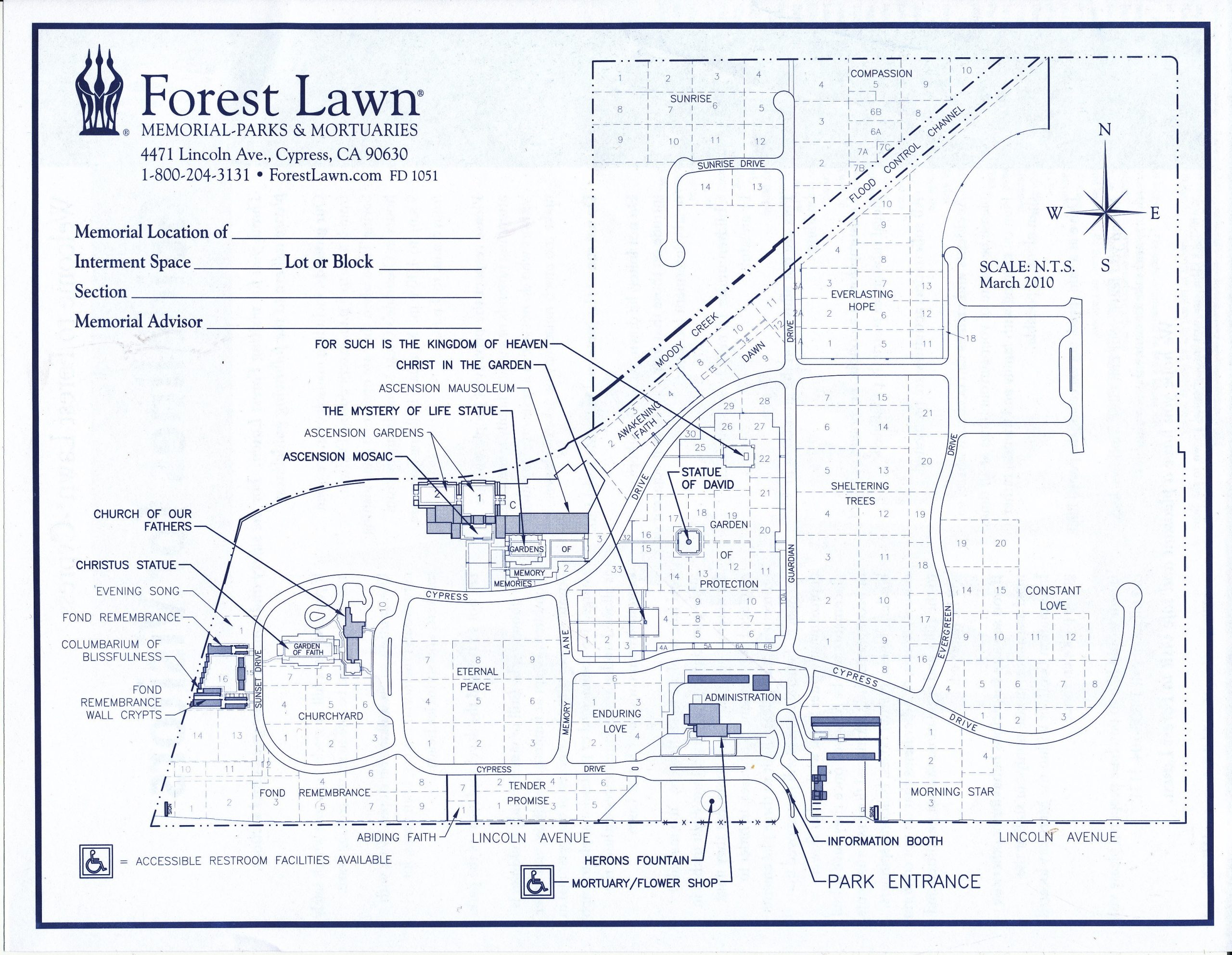
Grave Location:
Fond Remembrance, Lot 5027, Space 1Grave Location Description
Park near Columbarium of of Sweet Memories. Walk on the sidewalk to the front of the columbarium, then follow the sidewalk to the left, walking toward Fond Remembrance Wall Crypts. Pass the large tree on the left, and turn left at the fifth row. You’ll see a large niche for Newton Wright on the right. Aviation pioneer Joan Smith is the 45th memorial.
Grave Location GPS
33.8323764, -118.0609960Visiting The Grave:
Photos:
FAQ's
Read More About Joan Merriam Smith:
- Published Obituary
- Wikipedia Entry
- This Day in Aviation - Joan Merriam Smith
- Joan Merriam Smith - Aviator 1964 interview by KCRA-TV
- Team rediscovers how a 1964 Long Beach woman was the first to pilot a solo trip around the equator
- Fate on a Folded Wing - the Joan Merriam Smith Story
- A Piece of History - Legend Down



