Johann Strauss ll
Fun Facts
Most of the Strauss ll works that are performed today may once have existed in a slightly different form, as Eduard Strauss destroyed much of the original Strauss orchestral archives in a furnace factory in Vienna’s Mariahilf district in 1907. Eduard, then the only surviving brother of the three, took this drastic precaution after agreeing to a pact between himself and brother Josef that whoever outlived the other was to destroy their works. The measure was intended to prevent the Strauss family’s works from being claimed by another composer. This may also have been fueled by Strauss’s rivalry with another of Vienna’s popular waltz and march composers, Karl Michael Ziehrer.
Also lost to the ages, Eduard Strauss surprisingly wound up the Strauss Orchestra in February 1901 after concerts in 840 cities around the globe, and pawned the instruments. The orchestra’s last violins were destroyed in the firestorm of the Second World War.
Two museums in Vienna are dedicated to Johann Strauss II. His residence in the Praterstrasse, where he lived in the 1860s, is now part of the Vienna Museum. The Strauss Museum is about the whole family, with a focus on Johann Strauss II.
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Der Wiener Zentralfriedhof
1110 Wien
Simmeringer Hauptstraße 234, Vienna,
Austria
Europe
Map:
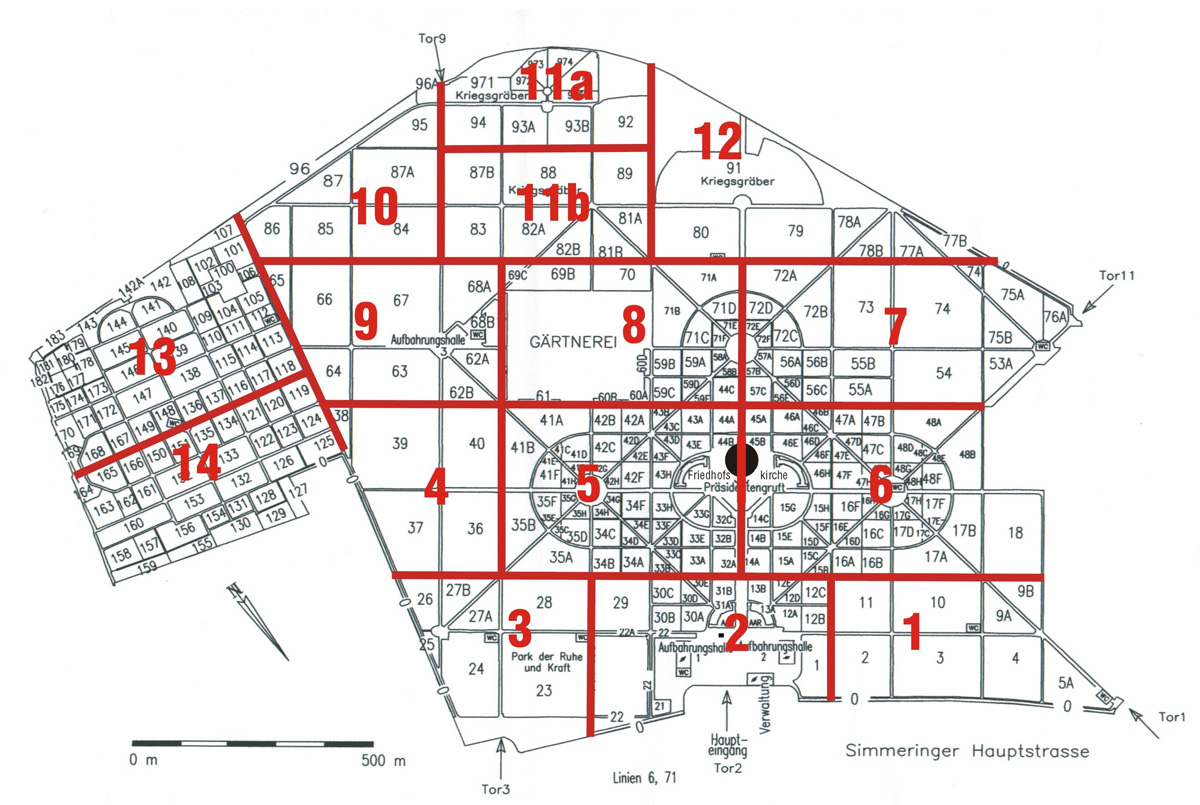
Grave Location:
Gruppe 32 A, Grab Nr. 27Grave Location Description
You can find the grave very easily if you enter the cemetery through that main entrance, which is called Tor (Gate) 2. Once inside, go straight on, through the middle of the stone arcade ahead of you, towards the large Jugendstil church in the distance. Just keep your eyes on the left hand side to eventually spot the grave of the legendary composer about 100 feet off the road. Nearby neighbors include Beethoven, Schubert, and Brahms. Across the paved path is a memorial to some guy named Mozart.








