Arnold Schoenberg
Interesting to Know
Schoenberg was also an influential teacher of composition; his students included Alban Berg, Anton Webern, Hanns Eisler, Egon Wellesz, Nikos Skalkottas and later John Cage, Lou Harrison, Earl Kim, Robert Gerhard, Leon Kirchner, Dika Newlin, Oscar Levant, and other prominent musicians. Many of Schoenberg’s practices, including the formalization of compositional method and his habit of openly inviting audiences to think analytically, are echoed in avant-garde musical thought throughout the 20th century.
The composer’s final days are documented in handwritten notes by his wife Gertrud, who meticulously recorded the progression of his illness and the daily routines, along with house visits by his physician Dr Orren Lloyd-Jones. On July 13, 1951 Schönberg did not eat at all and he received a sedative a few hours before his death. At 6 p.m. his pulse was 90, at 7:30 p.m. it was 72. At 11:45 p.m. Arnold Schönberg died with his wife beside him. His final word was “harmony.” On July 14 Anna Mahler took an impression of his face for the death mask.
Over the years since his passing, there has been made much about his anxiety due to triskaidekaphobia (fear of the number 13). Interesting to note that he died on Friday the 13th at the age of 76 (7+6=13).
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Der Wiener Zentralfriedhof
1110 Wien
Simmeringer Hauptstraße 234, Vienna,
Austria
Europe
Map:
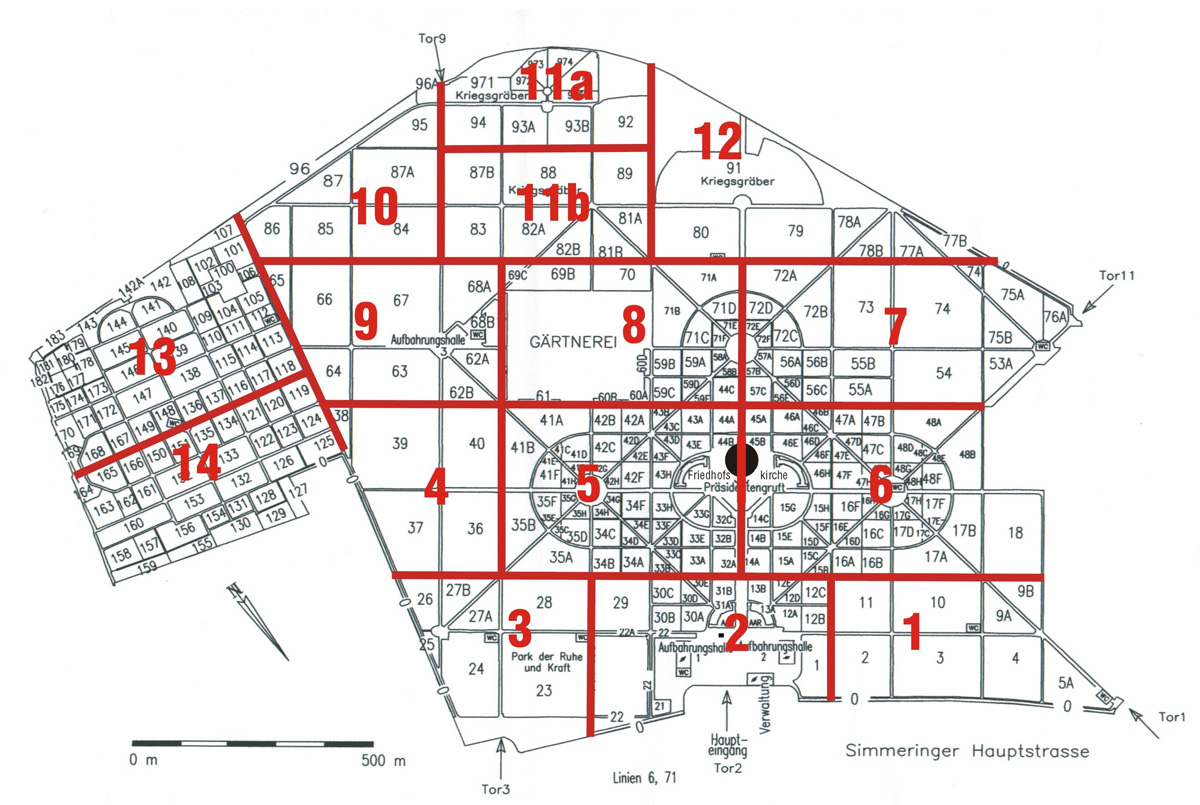
Grave Location:
Gruppa 32 C, Grab Nr. 21AGrave Location Description
As you enter the cemetery through Tor 2 (Gate 2) drive straight ahead towards The St. Charles Borromeo Cemetery Church in the middle of the Vienna Central Cemetery. As you approach the church take the last soft left turn and look to your left into Gruppa 32 C and you will find the large angled cube that marks the grave of Arnold Schoenberg.








