array(1) {
[0]=>
string(156) "Grave of Mark Sandman. Mark Sandman was born on September 24, 1952 and died in Giardini del Principe, Palestrina, Italy due to Heart attack on July 3, 1999."
}
array(1) {
[0]=>
string(174) "Grave of Bunk Johnson. Bunk Johnson was born on December 27, 1885 and died in 638 Franklin Street, New Iberia, Louisiana due to Lingering effects of a stroke on July 7, 1949."
}
Comte de Buffon was a French naturalist, mathematician, cosmologist, and encyclopédiste whose collective works influenced generations of naturalists including Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Georges Cuvier. He was considered by many to be the Father of all Thought in the field of natural history in the 18th century.
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Sainte-Urse de Montbard Church
Allée Clemenceau
Montbard, , 21500
France
Europe
Map:
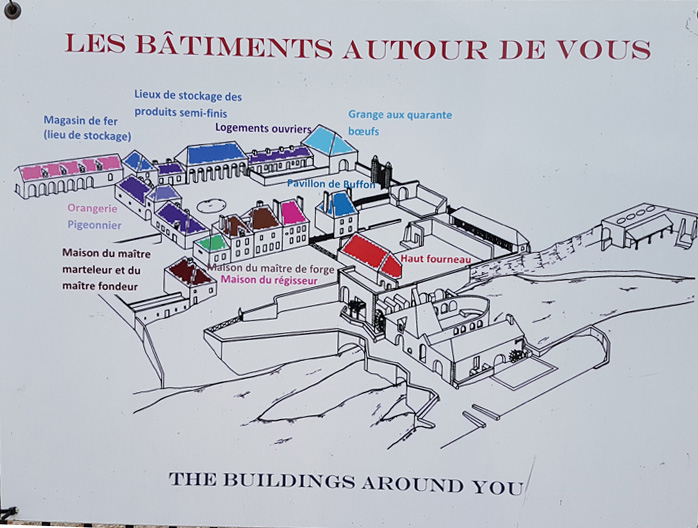
Map of La Grande Forge de Buffon
Grave Location:
Seigneurial chapel
Grave Location Description
On the south side of the church in the seigneurial chapel located on the grounds of La Grande Forge de Buffon.
Grave Location GPS
47.6253, 4.3355
Photos:
Read More About Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon:
Videos Featuring Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon:
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte De Buffon
Vidéo présentation Grande Forge de Buffon
Comte de Buffon Biography
See More:
Kurt Gödel
popular name: Kurt Gödel
date_of_death: January 14, 1978
age: 71
cause_of_death: Malnutrition and inanition caused by personality disturbance
claim_to_fame: Science
best_know_for: Kurt Gödel was a prominent Austrian/American logician, mathematician and philosopher who is mentioned as most likely autistic (Asperger's Syndrome) in Genius Genes by Michael Fitzgerald and Brendan O’Brien, in Asperger Syndrome – A Gift or a Curse? by Michael Fitzgerald and Viktoria Lyons. He is known in particular for Gödel's incompleteness theorems, Gödel's completeness theorem, the consistency of the Continuum hypothesis with ZFC, Gödel metric, Gödel's ontological proof and Gödel–Dummett logic, Among notable awards he has won are the Albert Einstein Award (1951), the National Medal of Science (1974) and ForMemRS (1968). He was also a Fellow of the British Academy. Looking back over that century in the year 2000, TIME magazine included Kurt Gödel (1906–78), the foremost mathematical logician of the twentieth century among its top 100 most influential thinkers. Gödel was associated with the Princeton University Institute for Advanced Study from his first visit in the academic year 1933–34, until his death in 1978. He was Professor in the School of Mathematics from 1953 until 1976, when he became Professor Emeritus.
Christa McAuliffe
popular name: Christa McAuliffe
date_of_death: January 28, 1986
age: 37
cause_of_death: Space shuttle accident
claim_to_fame: Science
best_know_for: Christa McAuliffe was an American teacher and astronaut from Concord, New Hampshire, who was killed on the Space Shuttle Challenger on mission STS-51-L where she was serving as a payload specialist. On January 28, 1986, McAuliffe boarded Challenger with the other six crew members of STS-51-L. Seventy-three seconds into its flight at an altitude of 48,000 ft (14.630 km), the shuttle broke apart, resulting in the deaths of all seven crew members. According to NASA, it was in part because of the excitement over her presence on the shuttle that the accident had such a significant effect on the nation. Many schoolchildren were viewing the launch live, and media coverage of the accident was extensive.
Edwin H. Land
popular name: Edwin H. Land
date_of_death: March 1, 1991
age: 81
cause_of_death: Undisclosed
claim_to_fame: Science
best_know_for: Edwin H. Land was an American scientist and inventor, best known as the co-founder of the Polaroid Corporation and the inventor of instant photography. “Dr. Land,’’ as most people referred to him, left Harvard College before graduation to start inventing in a Cambridge garage. In 40 years, Land built up a company that did about $1.4 billion of business all over the world in 1979 with over 20,000 employees. He stuck to his guns, never diversified into other businesses, never sold out to another company, and never borrowed money on a long-term basis. Land was awarded more than 500 patents, and other Polaroid researchers hundreds more. The Polaroid company was a juggernaut of innovation. In modern terms, Polaroid was the Apple of its time with a brilliant leader in Edwin Land, a scientist who guided the company as the CEO for several decades. But the company suffered a long decline starting in the ’80s leading to bankruptcy in the 2000s.
Back to Top




