Ludwig Boltzmann
Fun Facts
The formula on his tombstone, S = k log W, is the equation for the entropy of a system of particles. It states that entropy, which can be regarded as a measure of a system’s “disorder,” depends only on a constant number k (now named Boltzmann’s constant) and the number of possible “microstates” W. Microstates essentially describe the configurations of the locations and momenta of particles in a system.
In 1904 Boltzmann visited the World’s Fair in St Louis, USA. He lectured on applied mathematics and then went on to visit Berkeley and Stanford. Unfortunately he failed to realise that the new discoveries concerning radiation that he learnt about on this visit were about to prove his theories correct.
At sixty-two, suffering from incumbent blindness and other ailments, in the process of giving in to depression after the loss of his eldest son, his pride and self-esteem took a great toll owing to the criticism of many fellow scientists. Boltzmann then sought refuge and peace of mind in the small village of Duino, on the border of the Astro-Hungarian Empire. Neither the sunsets non the beautiful gulf nor Rilke’s verses helped him fend off the terrible depression that was devouring his soul and on a bleak day towards the end of the summer, on September 5th 1906 Boltzmann took his life by hanging himself from the window of his hotel room – formerly known as Hotel Ples now the one of the buildings of the United World College, opposite the Carabinieri station.
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Der Wiener Zentralfriedhof
1110 Wien
Simmeringer Hauptstraße 234, Vienna,
Austria
Europe
Map:
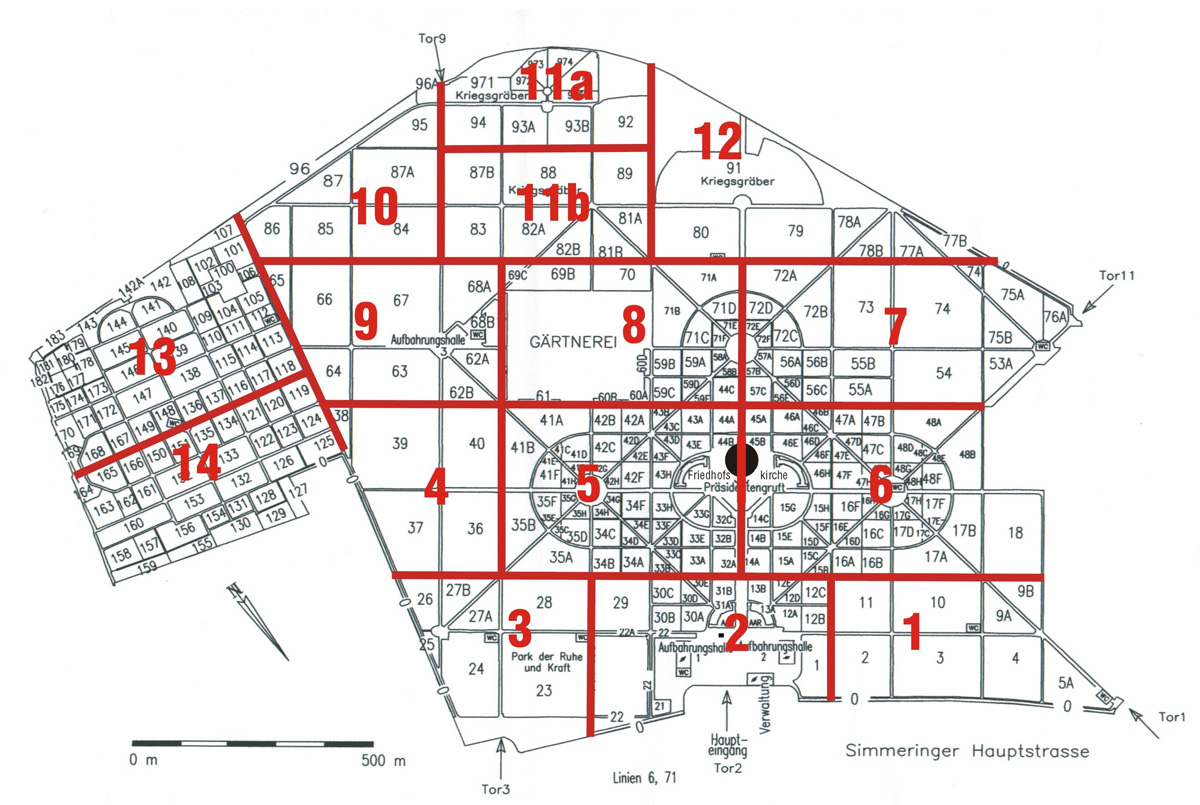
Grave Location:
Gruppe 14 C, Grab Nr. 1Grave Location Description
As you enter the cemetery through Tor 2 (Gate 2) drive straight ahead towards The St. Charles Borromeo Cemetery Church in the middle of the Vienna Central Cemetery. As you approach the church take the second to last right turn before the church and look to your left into Gruppa 14 C and you will find the large, unmistakable memorial to one of the greatest theoretical physicists of all time Ludwig Boltzmann.





