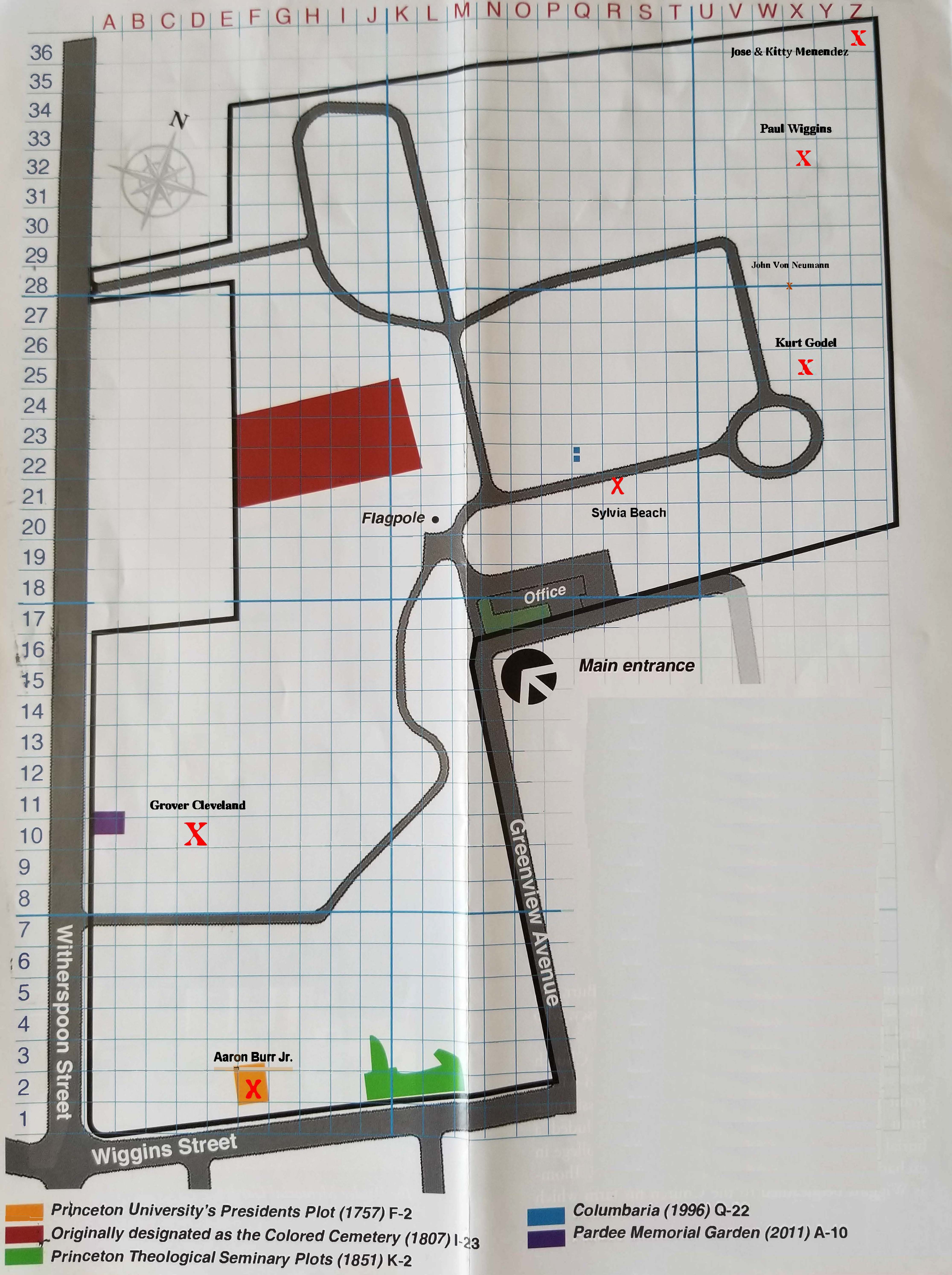
John von Neumann was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. Von Neumann was regarded as perhaps the mathematician with the widest coverage of the subject in his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in pure and applied mathematics". Von Neumann's academic career was filled with awards and honors. He was a Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences; Academiz Nacional de Ciencias Exactas, Peru; Acamedia Nazionale dei Lincei, Italy; National Academy of Sciences; Royal Netherlands Academy of Sciences and Letters; Information Processing Hall of Fame; and held numerous honorary degrees. Described as the scientific genius who pioneered the modern computer, game theory, nuclear deterrence, and more, John von Neumann illuminated the fields of pure and applied mathematics, computer science, physics, and economics. In the end, it would be supremely difficult to effectively refute the claim that John von Neumann is likely the most intelligent person who has ever lived. By the time of his death in 1957 at the modest age of 53, the Hungarian polymath had not only revolutionized several subfields of mathematics and physics but also made foundational contributions to pure economics and statistics and taken key parts in the invention of the atomic bomb, nuclear energy and digital computing.
Fun Fact
In Princeton, he received complaints for regularly playing extremely loud German march music on his phonograph, which distracted those in neighboring offices, including Albert Einstein, from their work.
Accepting an invitation from Oswald Veblen to lecture on quantum theory at Princeton University, John von Neumann was one of a group of Hungarian and Jewish intellectuals to escape to the United States from the turmoil of Europe. Following a year as a guest lecturer, he was appointed to the faculty. At age 30, he became the youngest professor at the Institute for Advanced Study, in the School of Mathematics, where he was frequently mistaken for a graduate student.