array(1) {
[0]=>
string(156) "Grave of Mark Sandman. Mark Sandman was born on September 24, 1952 and died in Giardini del Principe, Palestrina, Italy due to Heart attack on July 3, 1999."
}
array(1) {
[0]=>
string(174) "Grave of Bunk Johnson. Bunk Johnson was born on December 27, 1885 and died in 638 Franklin Street, New Iberia, Louisiana due to Lingering effects of a stroke on July 7, 1949."
}
Eugene Paul "E. P." Wigner was a Hungarian theoretical physicist who also contributed to mathematical physics. He obtained American citizenship in 1937, and received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963 "for his contributions to the theory of the atomic nucleus and the elementary particles, particularly through the discovery and application of fundamental symmetry principles". Wigner and Hermann Weyl were responsible for introducing group theory into physics, particularly the theory of symmetry in physics. Along the way he performed ground-breaking work in pure mathematics, in which he authored a number of mathematical theorems. In particular, Wigner's theorem is a cornerstone in the mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics.
Fun Fact
Wigner participated in a meeting with Leo Szilard and Albert Einstein that resulted in the Einstein-Szilard letter, which prompted President Franklin D. Roosevelt to initiate the Manhattan Project to develop atomic bombs. Wigner was afraid that the German nuclear weapon project would develop an atomic bomb first. During the Manhattan Project, he led a team whose task was to design nuclear reactors to convert uranium into weapons grade plutonium.
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Princeton Cemetery
29 Greenview Avenue
Princeton, New Jersey, 08542
USA
North America
Map:
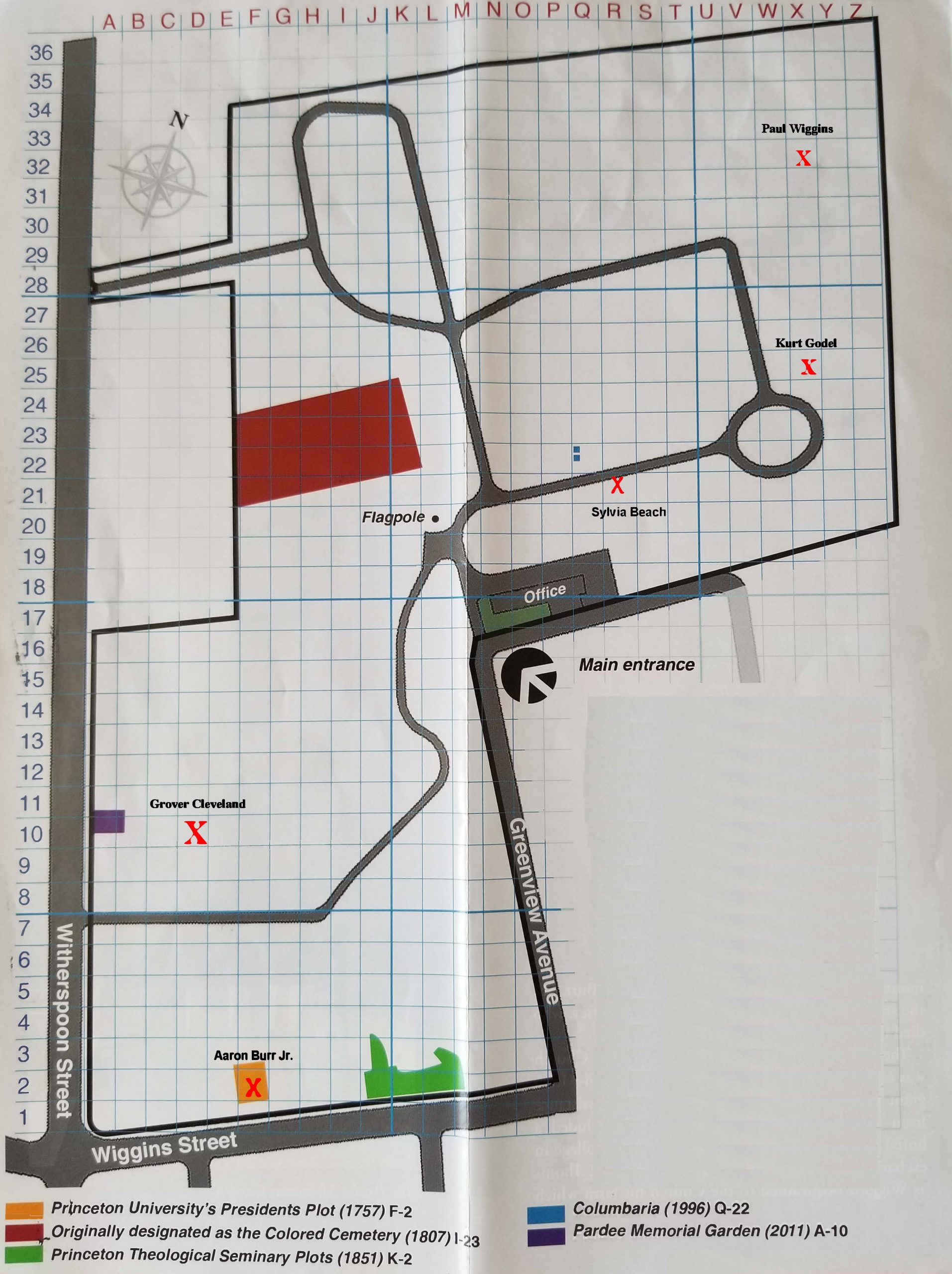
Grave Location:
Section 4, Block 31, Lot 31, Grave 1
Grave Location Description
As you drive through the entrance of the cemetery, past the office on your right, take the first right. Continue straight and stay to the right and drive 3/4 around the roundabout, bear right, and continue straight to the next curve and park. Walk to your right at an angle towards the far corner of the cemetery and E.P. Wigner’s upright monument should be visible about 150 feet from the road.
Grave Location GPS
40.35578057, -74.65905188
Photos:
Read More About Eugene Wigner:
Videos Featuring Eugene Wigner:
The Wigner's Friend paradox in 40 seconds
Wigner's Friend Paradox: Is Observation Inherently Flawed?
Eugene Wigner on John von Neumann
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics in the Natural Sciences
Eugene Wigner - The Quantum Mechanical Meaning of the Concept of Reality
Mathematics: The Language of God (Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics)
Edward Teller - An influence by Wigner and deciding to start a family
See More:
Dr. Henry Murray
popular name: Dr. Henry Murray
date_of_death: June 23, 1988
age: 95
cause_of_death: Pneumonia
claim_to_fame: Science
best_know_for: As the Director and Chief Researcher of the Psychological Clinic Annex on the campus of Harvard University, for 3 years beginning in 1959 Dr. Henry Murray was responsible for the unethical, immoral and horrible experiments in which he used 22 Harvard undergraduates as research subjects in psychological torture. The unwitting undergraduates were submitted to what Murray called "vehement, sweeping and personally abusive" attacks while strapped into a wooden chair with electrodes attached to their bodies. One of the subjects for the entire 3-year period was Ted Kaczynski, later known as the Unabomber who was responsible for killing 3 and maiming 23 other victims through his series of mail bombs.
Ludwig Boltzmann
popular name: Ludwig Boltzmann
date_of_death: September 5, 1906
age: 62
cause_of_death: Suicide - hanging
claim_to_fame: Science
best_know_for: Ludwig Boltzmann was one of the greatest theoretical physicists of all time. His fame is due to his pioneering research work on thermodynamics and statistical mechanics (his basic equation of kinetic gas theory and the second principle of thermodynamics) as well as the atomic hypothesis of matter. He also made important contributions in mechanics, electromagnetism, mathematics and philosophy. Boltzmann was an extraordinary mathematician, a philosopher, a great teacher (he had an outstanding memory), he was a brilliant conversationalist as well as an excellent pianist with a great passion for Beethoven. And yet he was a controversial figure and his innovative ideas (on atomism and irreversibility in particular) were often misunderstood and ostracized. In particular, his love of extreme mathematics earned him the by-name of "algebraic terrorist". Only a few years after his suicide that Jean Baptiste Perrin’s experimental verification of Brownian motion would settle the century-long debate about the atomic theory and thereby validate Boltzmann’s career.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
popular name: Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
date_of_death: April 16, 1788
age: 80
cause_of_death: Unkown
claim_to_fame: Science
best_know_for: Comte de Buffon was a French naturalist, mathematician, cosmologist, and encyclopédiste whose collective works influenced generations of naturalists including Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Georges Cuvier. He was considered by many to be the Father of all Thought in the field of natural history in the 18th century.
Back to Top