Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon
Birth Name:
Georges-Louis Leclerc
Birth Date:
September 7, 1707
Birth Place:
Montbard, Burgundy, France
Death Date:
April 16, 1788
Place of Death:
Paris, France
Age:
80
Cause of Death:
Unkown
Cemetery Name:
Sainte-Urse de Montbard Church
Claim to Fame:
Science
Comte de Buffon was a French naturalist, mathematician, cosmologist, and encyclopédiste whose collective works influenced generations of naturalists including Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Georges Cuvier. He was considered by many to be the Father of all Thought in the field of natural history in the 18th century.
Cemetery Information:
Final Resting Place:
Sainte-Urse de Montbard Church
Allée Clemenceau
Montbard, , 21500
France
Europe
Map:
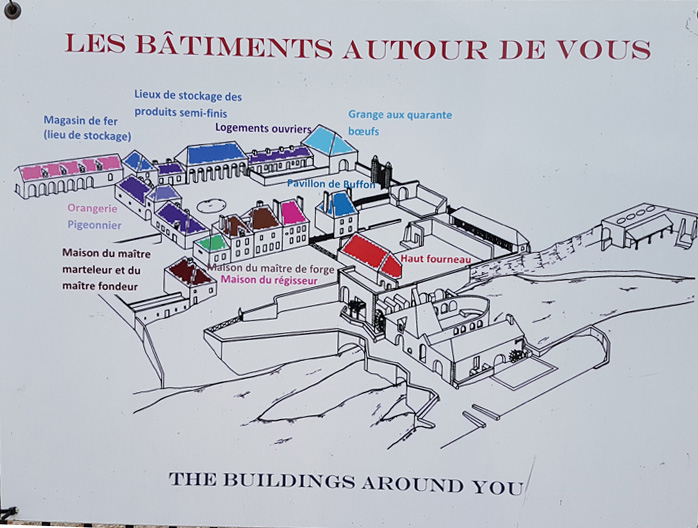
Map of La Grande Forge de Buffon
Grave Location:
Seigneurial chapelGrave Location Description
On the south side of the church in the seigneurial chapel located on the grounds of La Grande Forge de Buffon.
Grave Location GPS
47.6253, 4.3355Photos:
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
[+]
FAQ's
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon was born on September 7, 1707.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon was born in Montbard, Burgundy, France.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon died on April 16, 1788.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon died in Paris, France.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon was 80.
The cause of death was Unkown.
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon's grave is in Sainte-Urse de Montbard Church
Read More About Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon:
Videos Featuring Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon:
See More:
Back to Top



